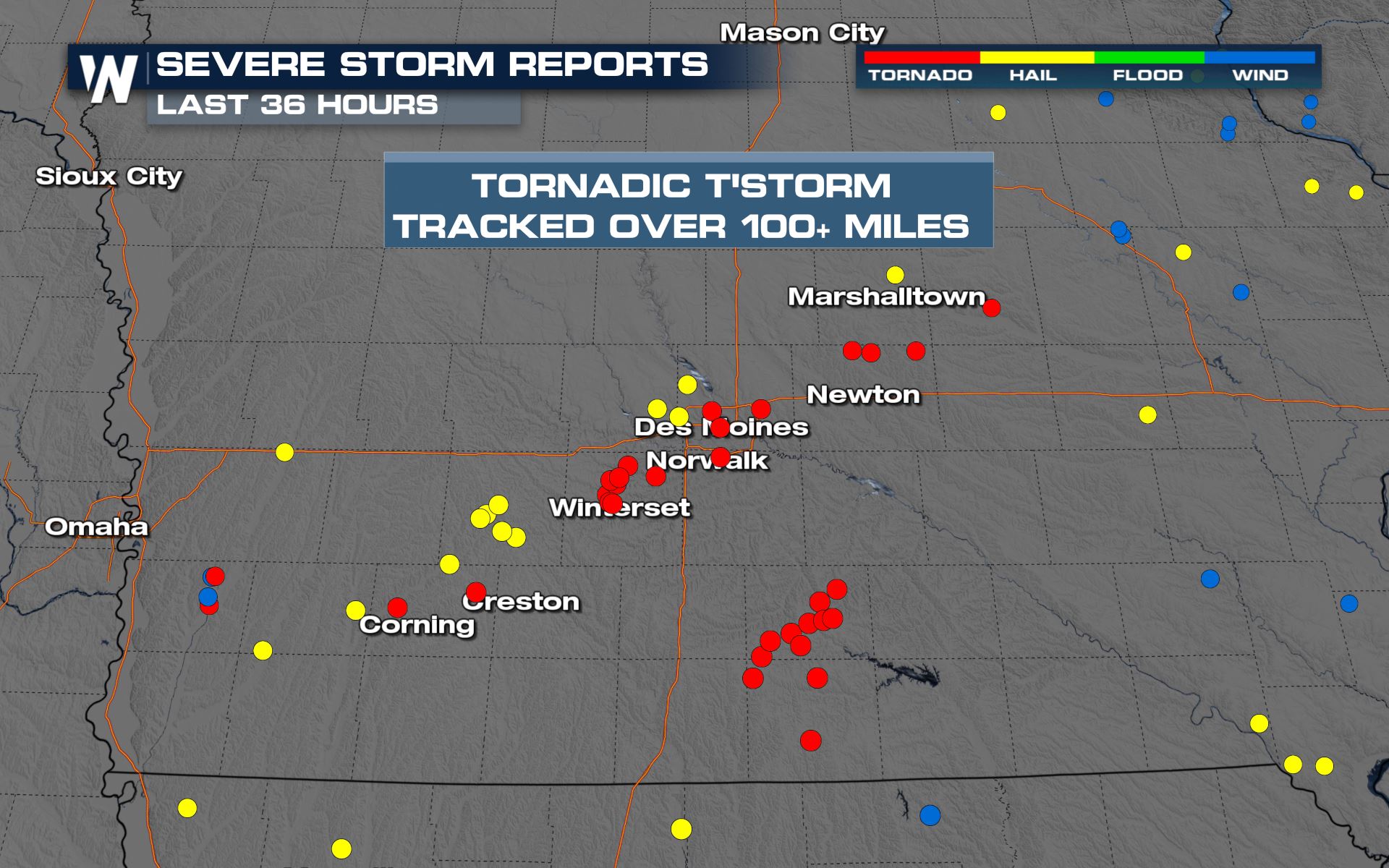
Iowa Tornado History
Iowa tornado map – Iowa, located in the heart of Tornado Alley, has a long and tumultuous history with these destructive storms. The state’s flat terrain and humid climate create a favorable environment for tornado formation, resulting in a frequency and severity that rank among the highest in the nation.
To stay informed about the latest tornado activity in Iowa, consult the Iowa Tornado Map for real-time updates. If you need immediate information on tornadoes occurring today, click here: iowa tornado today . Once you’ve checked the current status, return to the Iowa Tornado Map for ongoing tracking and updates.
The earliest recorded tornado in Iowa occurred in 1844, and since then, the state has witnessed countless devastating events. Some of the most significant tornado outbreaks in Iowa’s history include:
Notable Tornado Outbreaks
- 1878: The Sioux City tornado, an F5 tornado, killed 32 people and destroyed much of the city.
- 1965: The Palm Sunday tornado outbreak, a series of 47 tornadoes, killed 27 people and caused widespread damage across the state.
- 1975: The Waterloo tornado, an F5 tornado, killed 8 people and destroyed much of the city’s downtown.
- 2008: The Parkersburg tornado, an EF5 tornado, killed 6 people and caused extensive damage in the town of Parkersburg.
Impact on Iowa
Tornadoes have had a profound impact on Iowa’s landscape and communities. The storms have caused widespread destruction, loss of life, and economic devastation. The state’s agricultural industry, a vital part of its economy, has been particularly vulnerable to tornado damage.
In response to the frequent tornado threat, Iowa has developed a comprehensive emergency management system. The state has implemented early warning systems, established tornado shelters, and trained emergency responders to mitigate the impact of these storms.
Tornado Safety and Preparedness
Tornadoes can strike with little warning, making it crucial to be prepared and know what to do to stay safe. This section provides essential information on tornado warning systems, safety measures, and preparedness plans to help you stay informed and protected.
To stay informed about potential tornadoes, it is important to have multiple ways to receive warnings. NOAA Weather Radio broadcasts continuous weather information and alerts, including tornado warnings. Local television and radio stations also provide weather updates and warnings. Additionally, smartphone apps like the National Weather Service app can send notifications directly to your phone.
Recommended Safety Measures
When a tornado warning is issued, it is essential to take immediate action to seek shelter. The safest place to be during a tornado is in a sturdy building with a basement or interior room on the lowest floor. If there is no basement, go to an interior room on the lowest floor and stay away from windows.
If you are caught outside during a tornado, lie flat in a ditch or other low-lying area and cover your head with your hands. Do not seek shelter under bridges or overpasses, as these structures can collapse.
Iowa’s tornado map serves as an invaluable resource for tracking the latest severe weather activity. As tornadoes can strike with little warning, it’s essential to stay informed about current conditions. For the most up-to-date information on tornadoes in Iowa, visit our dedicated page on iowa tornado today . Our interactive map provides real-time updates on tornado warnings, watches, and past events, empowering you to make informed decisions and stay safe during severe weather.
Tornado Preparedness Plan
Creating a tornado preparedness plan for your home or business is crucial for ensuring the safety of everyone in the event of a tornado. Here are some key steps to consider:
- Identify a safe place in your home or business where you can take shelter during a tornado.
- Establish a communication plan with family members or employees to ensure everyone knows where to go and how to contact each other.
- Practice tornado drills with your family or employees to ensure everyone knows what to do in the event of a tornado warning.
li>Gather essential supplies, such as a first-aid kit, food, water, a battery-powered radio, and flashlights, and store them in an easily accessible location.
Tornado Forecasting and Tracking

Tornadoes are among the most destructive and unpredictable weather phenomena, making forecasting and tracking them crucial for public safety. Advances in technology have significantly improved our ability to predict and monitor these storms, providing valuable lead time for communities to prepare and respond.
Forecasting Methods
Tornado forecasting relies on a combination of weather observations, atmospheric modeling, and statistical analysis. Meteorologists use various data sources, including radar, satellite imagery, and weather station readings, to identify potential tornado-producing environments. Numerical weather prediction models simulate atmospheric conditions and can provide guidance on the likelihood and location of tornado development.
Tracking Technologies
Once a tornado has formed, real-time tracking is essential for issuing timely warnings and advising the public. Doppler radar is the primary tool for tornado detection and tracking. It measures wind speeds and directions within a storm, allowing meteorologists to identify rotating updrafts characteristic of tornadoes.
Accuracy and Limitations
Tornado forecasting and tracking have made significant progress in recent years, but there are still limitations. Forecasting lead times can vary depending on factors such as the storm’s speed and predictability. False alarms can occur, and tornadoes can sometimes develop rapidly with little warning.
Role of Technology
Technological advancements continue to play a crucial role in improving tornado forecasting and warning systems. Supercomputers with increased processing power allow for more sophisticated weather models and faster data analysis. Advanced radar systems, such as dual-polarization radar, provide more detailed information about storm structure, aiding in tornado detection.
Tornado Climatology
Iowa’s tornado climatology provides valuable insights into the frequency, intensity, and distribution of tornadoes across the state. Understanding these patterns is crucial for risk assessment, preparedness, and mitigation strategies.
To comprehensively analyze Iowa’s tornado climatology, we delve into data analysis, mapping, and trend identification, providing a comprehensive overview of this severe weather phenomenon.
Tornado Frequency and Intensity Across Iowa Regions
An in-depth analysis of tornado data reveals distinct patterns in frequency and intensity across different regions of Iowa. By organizing this data into a table, we can identify areas with higher tornado risks:
| Region | Average Annual Tornado Frequency | Average Tornado Intensity (EF Scale) |
|---|---|---|
| Northwest Iowa | 10-15 | EF2-EF3 |
| Central Iowa | 5-10 | EF1-EF2 |
| Southeast Iowa | 2-5 | EF0-EF1 |
This table demonstrates that northwest Iowa experiences the highest tornado frequency and intensity, while southeast Iowa has the lowest. These regional variations are influenced by factors such as terrain, atmospheric conditions, and prevailing wind patterns.
Tornado Distribution in Iowa Over Time
Mapping the distribution of tornadoes in Iowa over time allows us to visualize the spatial and temporal patterns of this phenomenon. By plotting tornado tracks on a map, we can identify areas that have been repeatedly impacted:
[Insert a map illustrating the distribution of tornadoes in Iowa over time]
This map reveals that tornadoes tend to occur in clusters, with certain areas experiencing multiple tornadoes within a short period. Additionally, the map shows that tornadoes can occur anywhere in Iowa, highlighting the need for statewide preparedness.
Seasonal and Annual Trends in Tornado Activity in Iowa
Analyzing seasonal and annual trends in tornado activity provides insights into the timing and frequency of these events. By examining historical data, we can identify peak tornado seasons and years:
- Tornado season in Iowa typically runs from April to June, with May being the most active month.
- The average annual number of tornadoes in Iowa is around 50, but this number can vary significantly from year to year.
- Iowa has experienced several notable tornado outbreaks, including the 2008 Parkersburg tornado and the 2011 Joplin tornado.
Understanding these trends helps us better anticipate and prepare for tornado events, ensuring the safety of Iowa communities.
Tracking the path of tornadoes across Iowa is crucial for staying informed and safe. The Iowa Tornado Map provides real-time updates, allowing you to monitor the Greenfield tornado and other severe weather events. By staying alert and using the map, you can take necessary precautions and stay out of harm’s way.
Tornado Research and Mitigation
Understanding and mitigating tornadoes requires ongoing research and concerted efforts. Researchers delve into various aspects of tornadoes, including their formation, behavior, and impacts, to improve prediction and preparedness measures.
Government agencies, such as the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), play a crucial role in tornado research and mitigation. They conduct studies, collect data, and develop forecasting tools to enhance tornado detection and warning systems.
The Iowa tornado map provides a comprehensive overview of past and present tornado activity in the state. For up-to-date information on any current tornado threats, please refer to the iowa tornado today page. The Iowa tornado map is an invaluable resource for staying informed about this potentially dangerous weather phenomenon.
Tornado Mitigation Strategies
Tornado mitigation strategies aim to reduce the vulnerability of communities and infrastructure to tornado impacts. Building codes that enforce tornado-resistant construction standards are vital in minimizing structural damage.
Early warning systems, such as tornado sirens and mobile phone alerts, provide timely notifications to residents, allowing them to seek shelter and avoid hazardous areas. Public education campaigns raise awareness about tornado safety and preparedness measures, empowering individuals to take proactive steps.
The effectiveness of tornado mitigation strategies has been evident in reducing casualties and property damage. However, continuous research and improvement are necessary to enhance their capabilities and adapt to changing environmental conditions.
Tornado Impact on Infrastructure and Economy: Iowa Tornado Map
Tornadoes, with their destructive force, pose significant threats to infrastructure and the economy. Iowa, being prone to tornadoes, has witnessed the devastating impact of these storms.
The destructive power of tornadoes can severely damage infrastructure, including buildings, roads, bridges, power lines, and communication networks. These damages disrupt essential services, hinder transportation, and lead to economic losses. Moreover, tornadoes can cause widespread power outages, affecting businesses, industries, and daily life. The loss of power can halt production, disrupt supply chains, and cause significant financial losses.
Economic Impact on Businesses and Industries
Tornadoes can have severe economic consequences for Iowa’s businesses and industries. The damage to infrastructure can disrupt supply chains, leading to delays and increased costs. Businesses may also experience losses due to property damage, inventory loss, and business interruption. The agricultural sector, a vital part of Iowa’s economy, is particularly vulnerable to tornado damage, with crops and livestock being susceptible to destruction.
If you’re seeking to track the unpredictable paths of Iowa’s twisters, an Iowa tornado map can serve as your trusted guide. From the bustling cities to the serene countryside, these maps provide real-time updates on the whereabouts of these formidable forces of nature.
And if you’re curious to delve deeper into the history and impact of Iowa tornados , there’s a wealth of information available at your fingertips. By harnessing the power of these maps, you’ll stay informed and prepared, ensuring your safety during Iowa’s tornado season.
Strategies for Reducing Economic Impact
Mitigating the economic impact of tornadoes requires a comprehensive approach. Strengthening infrastructure, such as constructing tornado-resistant buildings and reinforcing power lines, can reduce damage and minimize disruption. Early warning systems and timely evacuation plans can help protect lives and property. Additionally, businesses can implement disaster preparedness plans, including securing inventory, backing up data, and having insurance coverage in place to recover from tornado-related losses.
Tornado Awareness and Education
Public awareness campaigns are crucial for educating communities about the risks and preparedness measures associated with tornadoes. These campaigns utilize various channels, such as television, radio, print media, and social media, to disseminate information on tornado safety, warning systems, and evacuation plans. Additionally, schools and community organizations play a vital role in tornado education by incorporating age-appropriate materials into their curricula and organizing community events that promote preparedness.
Tornado Drills and Simulations, Iowa tornado map
Tornado drills and simulations are essential components of tornado preparedness. These exercises help individuals practice protective actions, such as seeking shelter in designated safe areas and following evacuation procedures. By participating in drills and simulations, individuals can become more familiar with their surroundings and identify potential hazards, thereby increasing their chances of survival in the event of a tornado.
Tornado Case Studies
Tornadoes are a common occurrence in Iowa, and they can cause significant damage and loss of life. By studying past tornado events, we can learn more about how they form, how they behave, and how to better prepare for them.
One of the most destructive tornadoes in Iowa history occurred on May 25, 2011. The tornado touched down near Sioux City and traveled for over 100 miles, leaving a path of destruction in its wake. The tornado was rated an EF-5, the highest rating on the Enhanced Fujita Scale, and it caused an estimated $2 billion in damage.
The May 25, 2011 tornado was a powerful and deadly event, but it also provided valuable lessons that have helped us to better understand tornadoes and how to prepare for them. By studying this tornado and other past events, we can continue to improve our tornado preparedness and mitigation efforts and reduce the risk of future damage and loss of life.
Factors Contributing to the Severity of the Tornado
There were several factors that contributed to the severity of the May 25, 2011 tornado. These factors included:
- The strength of the thunderstorm: The tornado formed in a very strong thunderstorm with high winds and a lot of instability. This provided the tornado with the energy it needed to become so powerful.
- The length of time the tornado stayed on the ground: The tornado stayed on the ground for over an hour, which gave it time to cause a lot of damage.
- The path of the tornado: The tornado traveled through a heavily populated area, which resulted in a lot of damage and loss of life.
Lessons Learned from the Event
The May 25, 2011 tornado taught us several important lessons about tornadoes. These lessons include:
- Tornadoes can be very powerful and destructive: Even a small tornado can cause significant damage, and a large tornado can be devastating.
- It is important to be prepared for tornadoes: Everyone should have a tornado preparedness plan in place, and they should know what to do if a tornado warning is issued.
- Tornado warnings should be taken seriously: When a tornado warning is issued, it is important to take shelter immediately.
How the Lessons Learned Have Influenced Tornado Preparedness and Mitigation Efforts
The lessons learned from the May 25, 2011 tornado have helped to improve tornado preparedness and mitigation efforts in Iowa. These efforts include:
- Increased public awareness of tornadoes: The tornado helped to raise public awareness of the dangers of tornadoes and the importance of being prepared.
- Improved tornado warning systems: The tornado helped to identify weaknesses in the tornado warning system, and these weaknesses have been addressed.
- Increased funding for tornado research: The tornado helped to secure funding for tornado research, which is helping us to better understand tornadoes and how to mitigate their effects.